
Pin on Microscopy
A diagram showing a leaf at increasing magnifications. Magnification 1: The entire leaf Magnification 2: Mesophyll tissue within the leaf Magnification 3: A single mesophyll cell Magnification 4: A chloroplast within the mesophyll cell Magnification 5: Stacks of thylakoids—grana—and the stroma within a chloroplast

Dicot leaf Biology plants, Plant science, Plant physiology
Leaves and photosynthesis Video - Leaf structure Video Transcript Photosynthesis is a vital process that occurs in the leaves of a plant. During photosynthesis, the leaves use chlorophyll and.

Leaf anatomy vector illustration diagram Aulas de biologia, Educação, Anatomia
leaf, in botany, any usually flattened green outgrowth from the stem of a vascular plant. As the primary sites of photosynthesis, leaves manufacture food for plants, which in turn ultimately nourish and sustain all land animals. Botanically, leaves are an integral part of the stem system.

Leaf Structure photo Botany, Teaching biology, Biology
The air space found between the spongy parenchyma cells allows gaseous exchange between the leaf and the outside atmosphere through the stomata. In aquatic plants, the intercellular spaces in the spongy parenchyma help the leaf float. Both layers of the mesophyll contain many chloroplasts. Figure 30.10. 1: Mesophyll: (a) (top) The central.
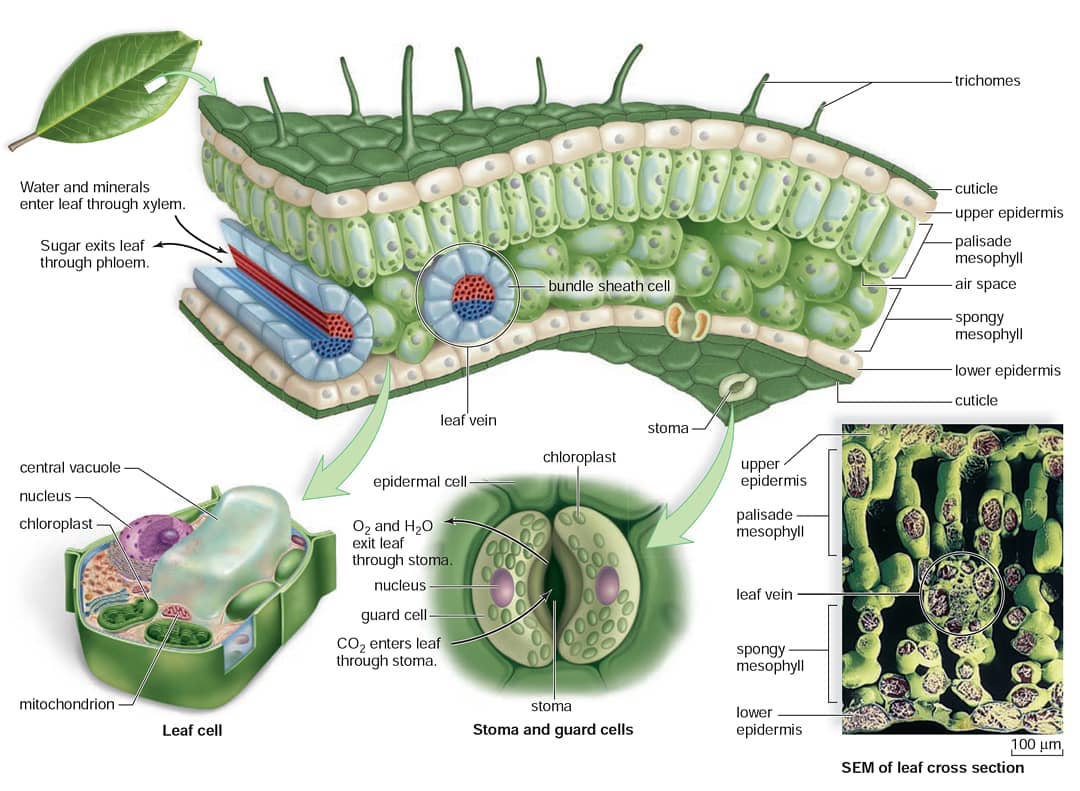
Structure of a leaf
Lára has a particular interest in the area of infectious disease and epidemiology, and enjoys creating original educational materials that develop confidence and facilitate learning. Download notes on. FREE Biology revision notes on Characteristics. Designed by the teachers at SAVE MY EXAMS for the CIE IGCSE Biology 0610 / 0970 syllabus.
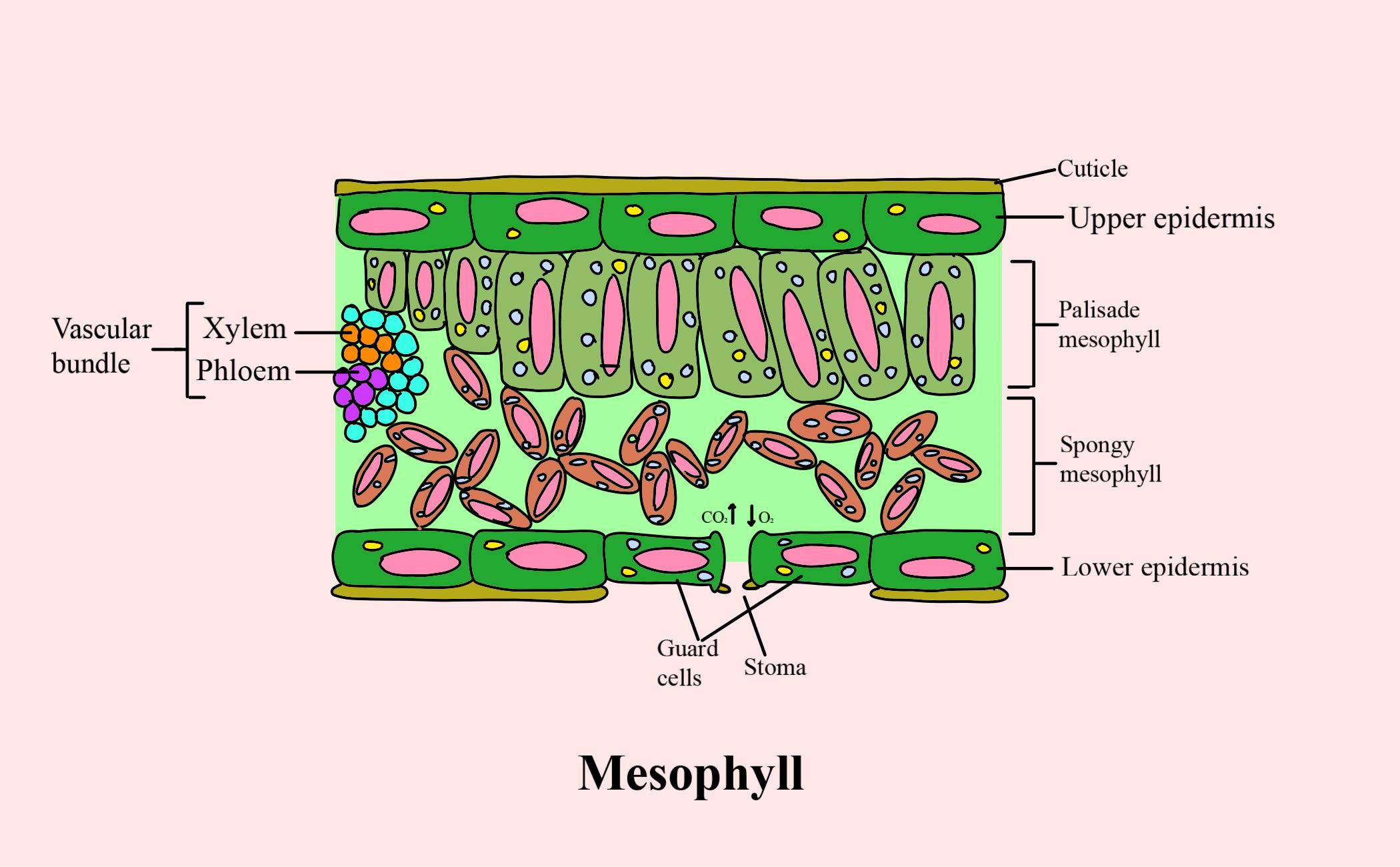
The mesophyll of leaf consists of (a) Spongy parenchyma cells (b) Palisade parenchyma cells(c
1 Cellular Structure of a Tree Leaf Tissue Structure of Tree Leaf. By Zephyris - commons.wikimedia.org Leaves are food factories for the tree. Powered by sunlight, the green substance in leaves.

Leaf Structure, Types, Functions GCSE Biology Revision
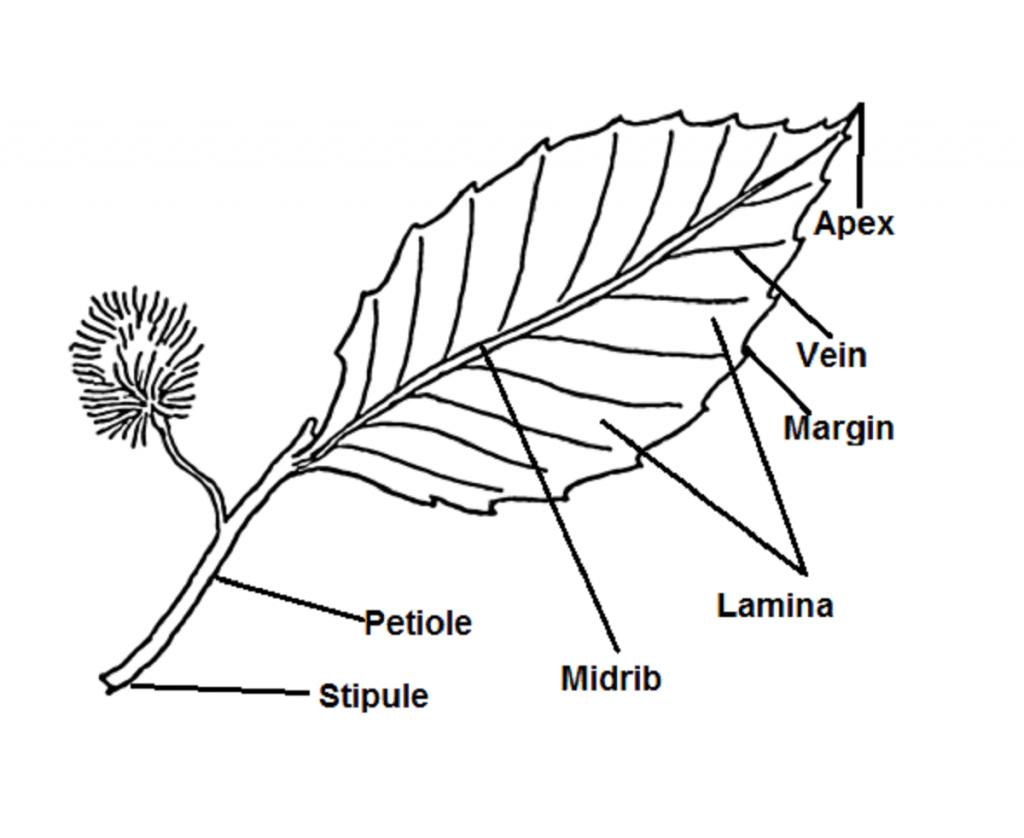
Definition of a Leaf: The leaf is a flattened, lateral outgrowth of the stem in the branch, developing from a node and having a bud in its axil. It is normally green in colour and manufactures food for the whole plant. The leaves take up water and carbon dioxide and convert them into carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
Ncert class 6 Science Getting to Know Plants Exercise answer Studdy
Figure 9.3. 2: Cross section of a hydrophytic leaf. Observe a prepared slide of a hydrophyte, such as Nymphaea, commonly called a water lily. Note the thin epidermal layer and the absence of stomata in the lower epidermis. In the spongy mesophyll, there are large pockets where air can be trapped.

Cross Section of a Leaf Biology Diagram
Figure 30.8.1 30.8. 1: Parts of a leaf: A leaf may seem simple in appearance, but it is a highly-efficient structure. Petioles, stipules, veins, and a midrib are all essential structures of a leaf. Within each leaf, the vascular tissue forms veins. The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called the venation pattern.
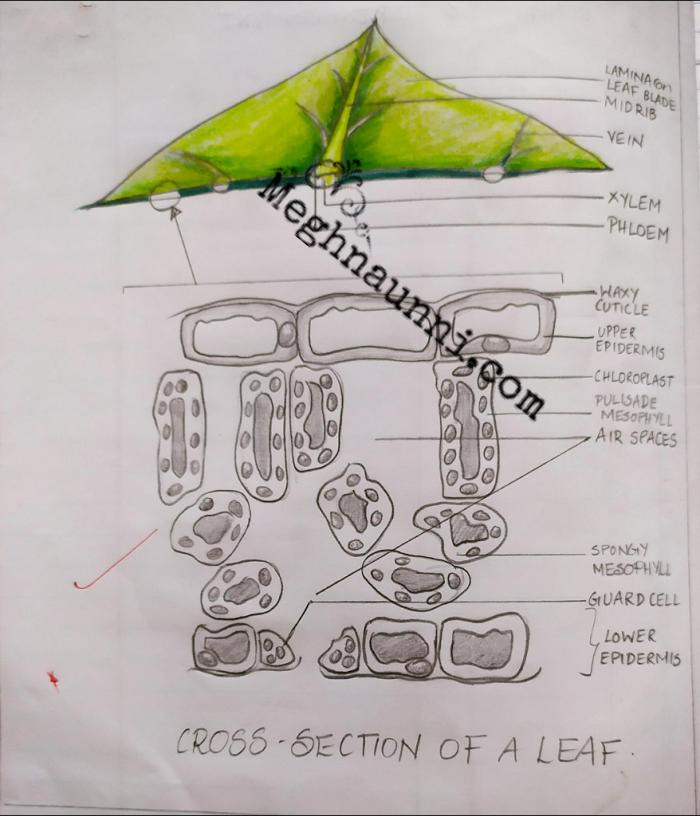
Cross Section of a Leaf Biology Diagram
Leaf Parts. Leaves are generally composed of a few main parts: the blade and the petiole. Figure 13.1.2 13.1. 2: A leaf is usually composed of a blade and a petiole. The blade is most frequently the flat, photosynthetic part. The petiole is a stem that attaches the leaf blade to the main stem of the plant.
leaf structure Labelled diagram
The structure of a leaf The leaves are the organ for photosynthesis. It is where photosynthesis takes place. The structures of leaves are adapted for efficient photosynthesis as shown in the table below. The cellular structure of a leaf Next: Factors affecting the rate of Photosynthesis
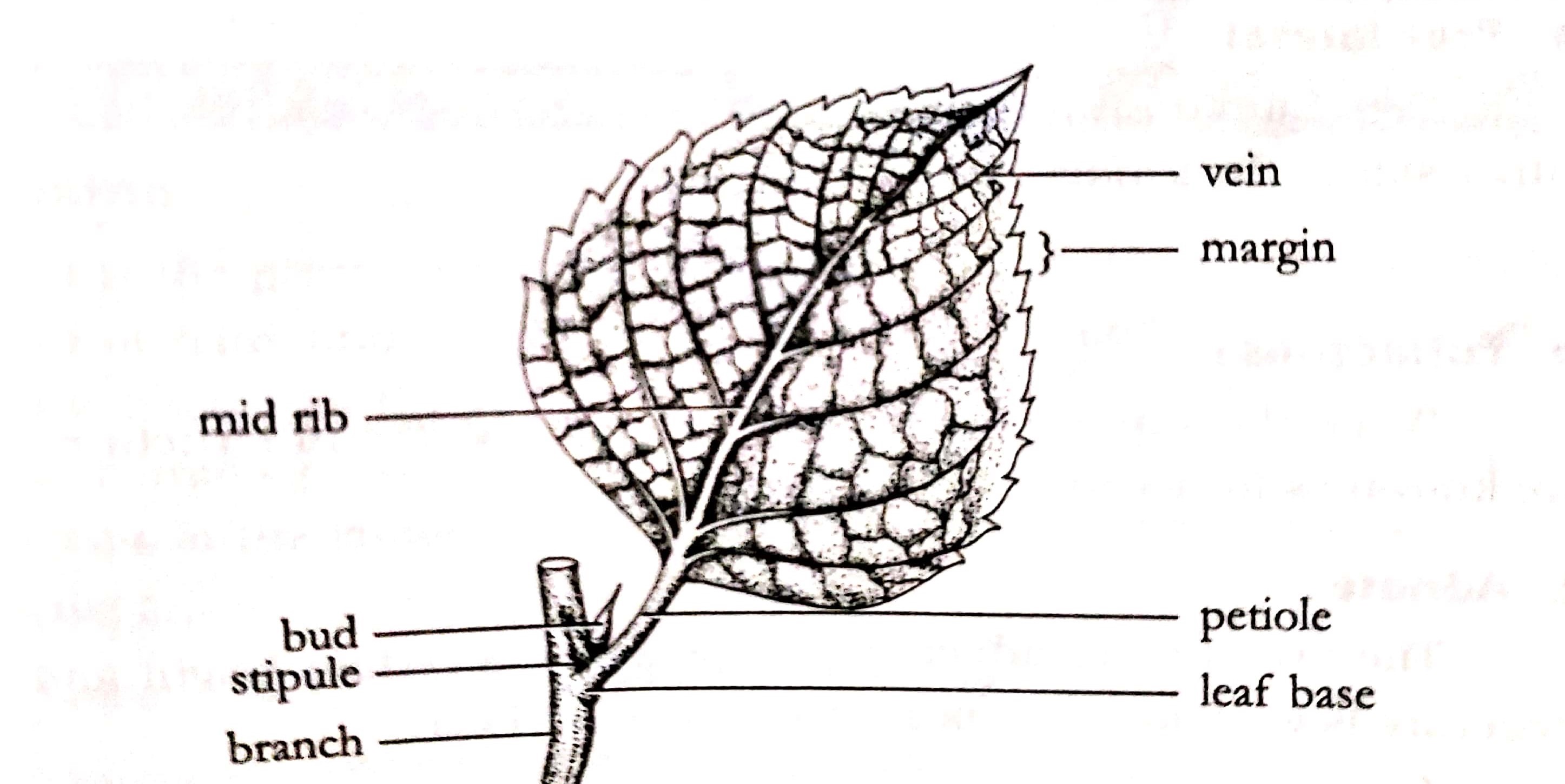
A typical plant leaf (Different parts and types) Online Science Notes
Expand/collapse global hierarchy. Bookshelves. Botany and Horticulture. Botany Lab Manual (Morrow) 9: Leaf Anatomy. 9.2: Introduction to Leaf Anatomy. Expand/collapse global location.

Pin by Kajal Kumari on biology Biology plants, Teaching biology, Biology lessons
A leaf diagram representing the parts of a leaf Read more: Types of Stipules Venation Venation is defined as the arrangement of veins and the veinlets in the leaves. Different plants show different types of venation. Generally, there are two types of venation:
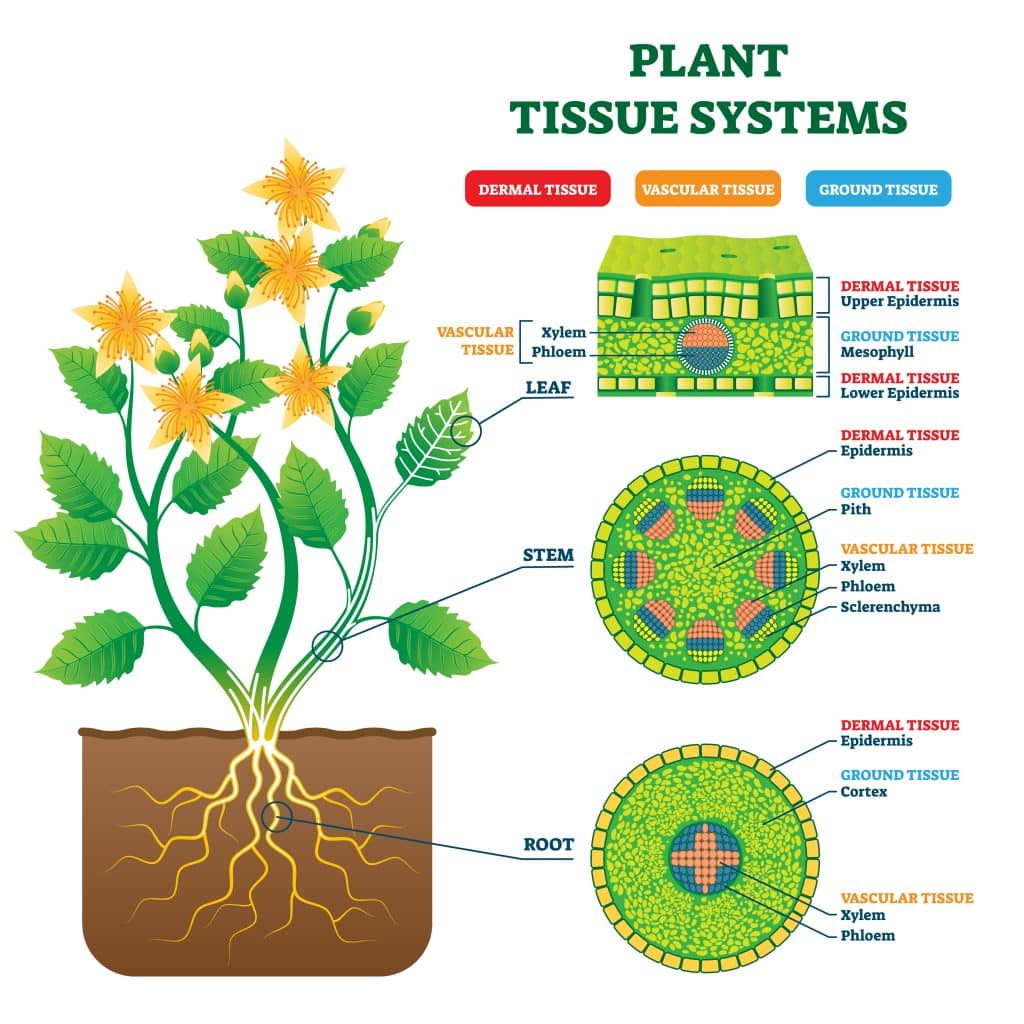
Section 5 Roots, Stems, and Leaves Nitty Gritty Science
Like the stem, the leaf contains vascular bundles composed of xylem and phloem (Figure 3.4.2.6 − 7 3.4.2. 6 − 7 ). When a typical stem vascular bundle (which has xylem internal to the phloem) enters the leaf, xylem usually faces upwards, whereas phloem faces downwards. The conducting cells of the xylem (tracheids and vessel elements.

Plant Structures Biology for Majors II
WJEC Structure of plants - WJEC Leaf structure Plants adapt in order to efficiently collect raw materials required for photosynthesis. These raw materials must be transported through the plant.
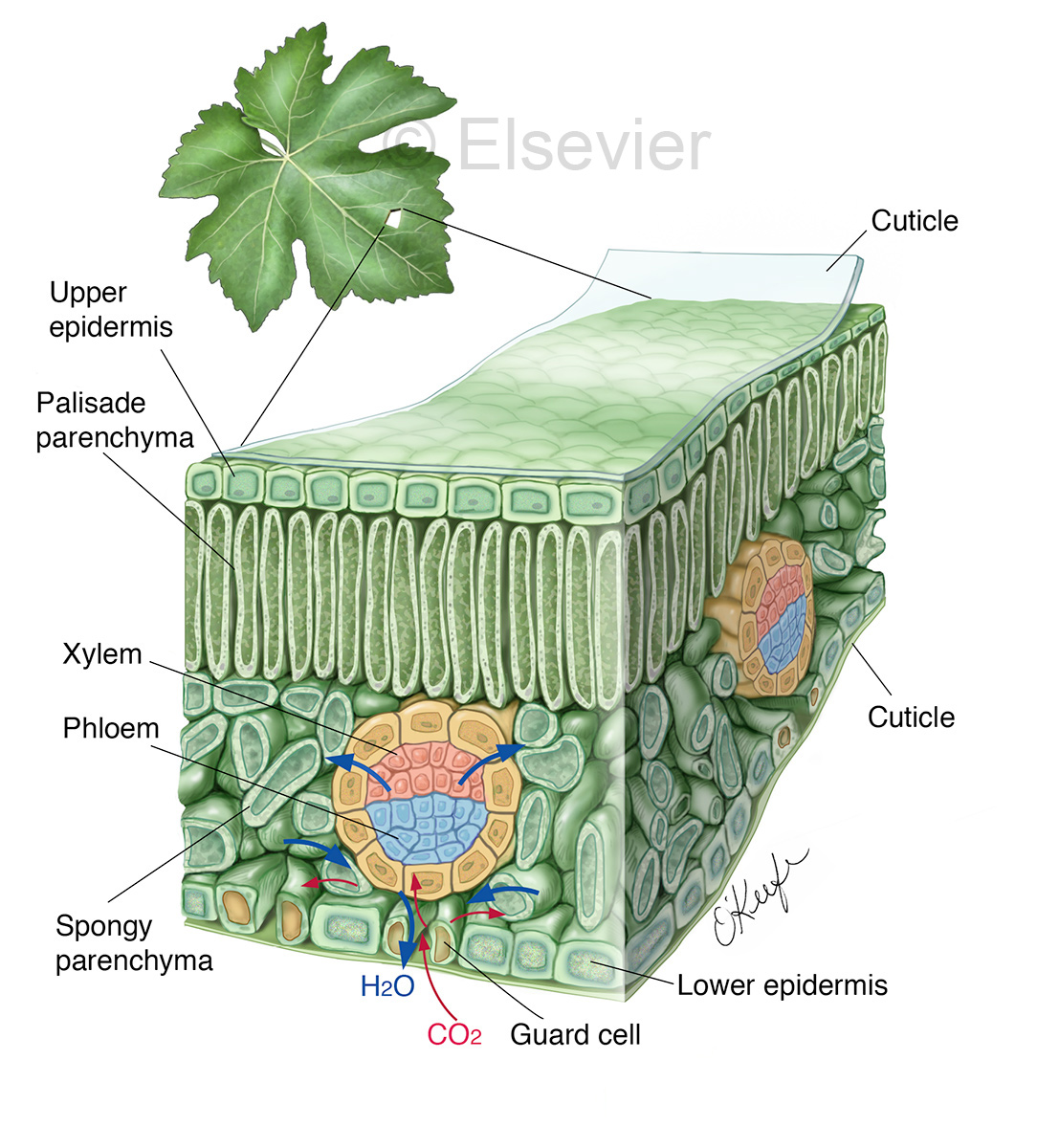
Biomedical Illustrator Medical & Biological Illustrations Laurie O’Keefe
A leaf is a highly organized factory - an organ constructed of several kinds of specialized tissues, each of which has its own duties.