
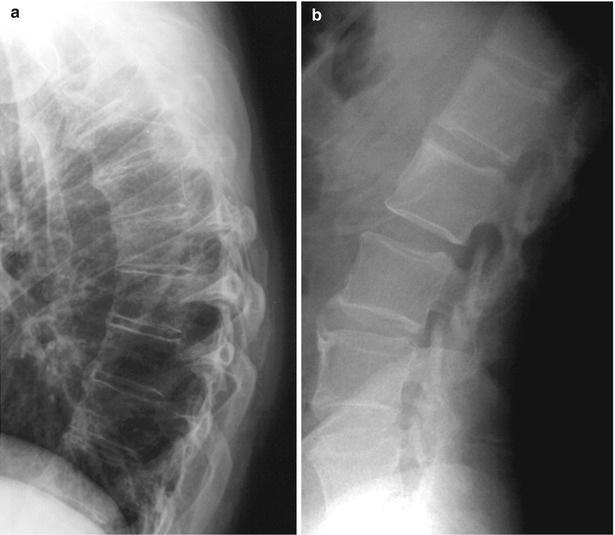
Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis BMJ Case Reports
Ankylosing spondylitis (less commonly known as Bechterew disease or Marie Strümpell disease ) is a seronegative spondyloarthropathy , which results in fusion (ankylosis) of the spine and sacroiliac (SI) joints, although involvement is also seen in large and small joints. Epidemiology
Ankylosing Spondylitis Mri
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the spinal and sacroiliac joints, which link the pelvis and spine. Fusion (ankylosis) of the spine's vertebrae, which happens over time, is a hallmark sign of this disease.

Ankylosing Spondylitis Radsource
The earliest signs of spondylitis are manifest as small erosions at the corners of the vertebral bodies - the so-called Romanus lesion. Syndesmophyte formation eventually lead to classical 'bamboo spine'. Osteoporosis and kyphosis occur with long-standing disease. Extra-axial skeletal involvement mimics mild rheumatoid arthritis.

Ankylosing spondylitis. Xray AP (a) and lateral (b) lumbar spine.... Download Scientific Diagram
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatologic disorder that predominantly affects the axial skeleton and is characterized by sacroiliitis, spondylitis and enthesitis.

Image
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the spine and the sacroiliac joints. AS occurs with the inflammation of the entheses and formation of syndesmophytes and finally sacral and spinal ankylosis. Imaging demonstrates both inflammatory and chronic lesions. Sacroiliitis is the hallmark of the disease. Spinal changes usually take place in advanced stages of the.
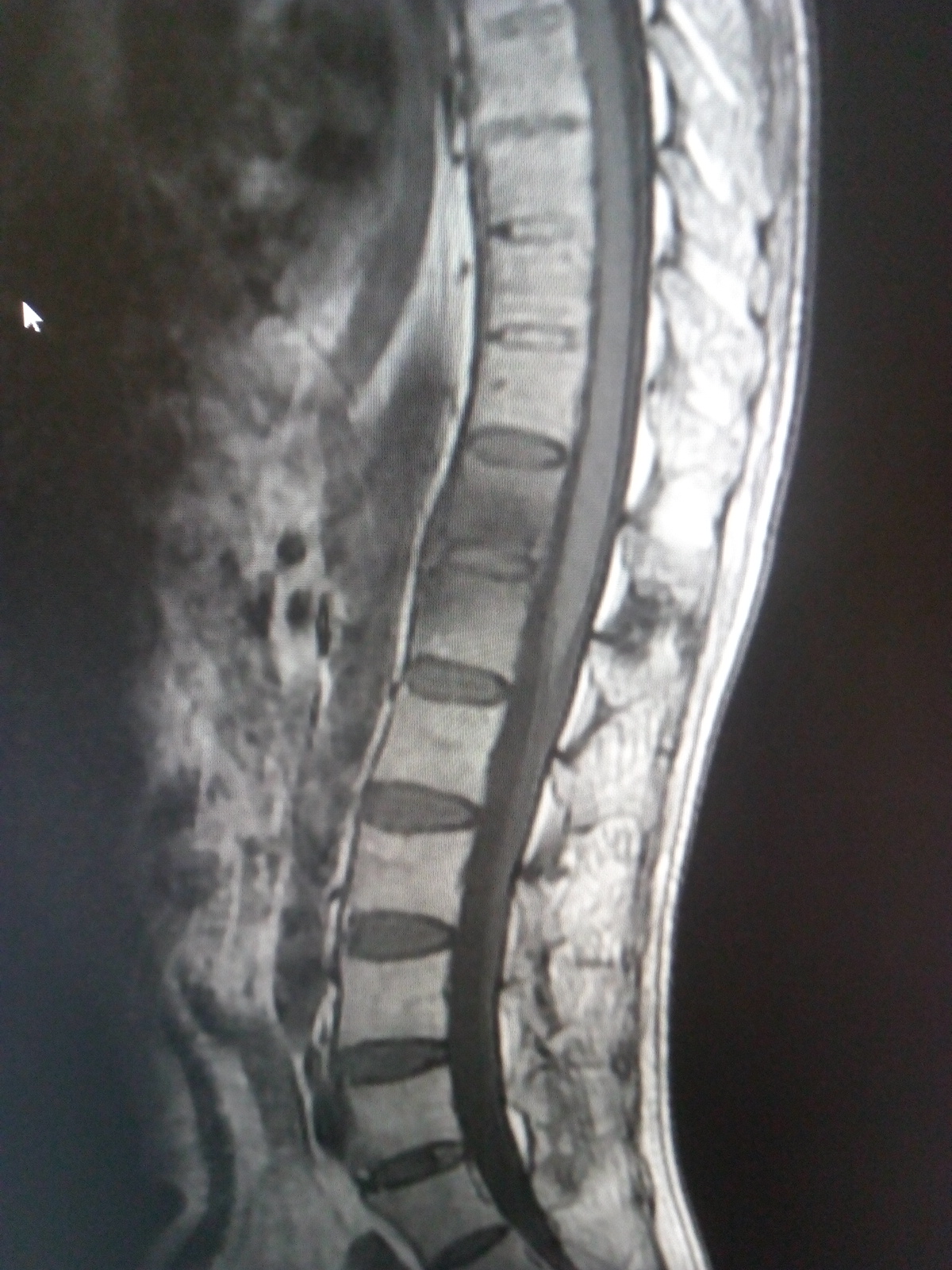
Ankylosing Spondylitis MRI Sumer's Radiology Blog
CT scan X-ray Treatment The goal of treatment is to relieve pain and stiffness and prevent or delay complications and spinal deformity. Ankylosing spondylitis treatment is most successful before the disease causes irreversible damage. Medications

Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Key
Ankylosing spondylitis is the most common seronegative spondyloarthropathy. It has characteristic radiological features.

Ankylosing spondylitis lumbar spine Image
Purpose To re-examine the patterns of radiographic involvement in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Materials and Methods This prospective study had institutional review board approval, and 769 patients with AS (556 men, 213 women; mean age, 47.1 years; age range, 18-87 years) provided written informed consent.

Images
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic, inflammatory disease of the axial spine. Chronic back pain and progressive spinal stiffness are the most common features of this disease. Involvement of the spine, sacroiliac joints, peripheral joints, digits, and entheses are characteristic.

Imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Mikkel Østergaard, Robert G.W. Lambert, 2012
Imaging is an integral part of the management of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and axial spondyloarthritis. Characteristic radiographic and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings are key in the diagnosis. Radiography and MRI are also useful in monitoring the disease.

Ankylosing Spondylitis MRI Sumer's Radiology Blog
Preferred examination Radiographs are the single most important imaging technique for the detection, diagnosis, and follow-up monitoring of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Overall bony.

Image
Abstract. Imaging has a central role in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). For the early diagnosis of axSpA, magnetic resonance imaging is of utmost relevance. While no novel imaging techniques were developed during the past decade, improvements to the existing modalities have been introduced.

Ankylosing Spondylitis MRI Sumer's Radiology Blog
Objective: To update evidence-based recommendations for the treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (SpA). Methods: We conducted updated systematic literature reviews for 20 clinical questions on pharmacologic treatment addressed in the 2015 guidelines, and for 26 new questions on pharmacologic treatment, treat-to-target strategy, and.
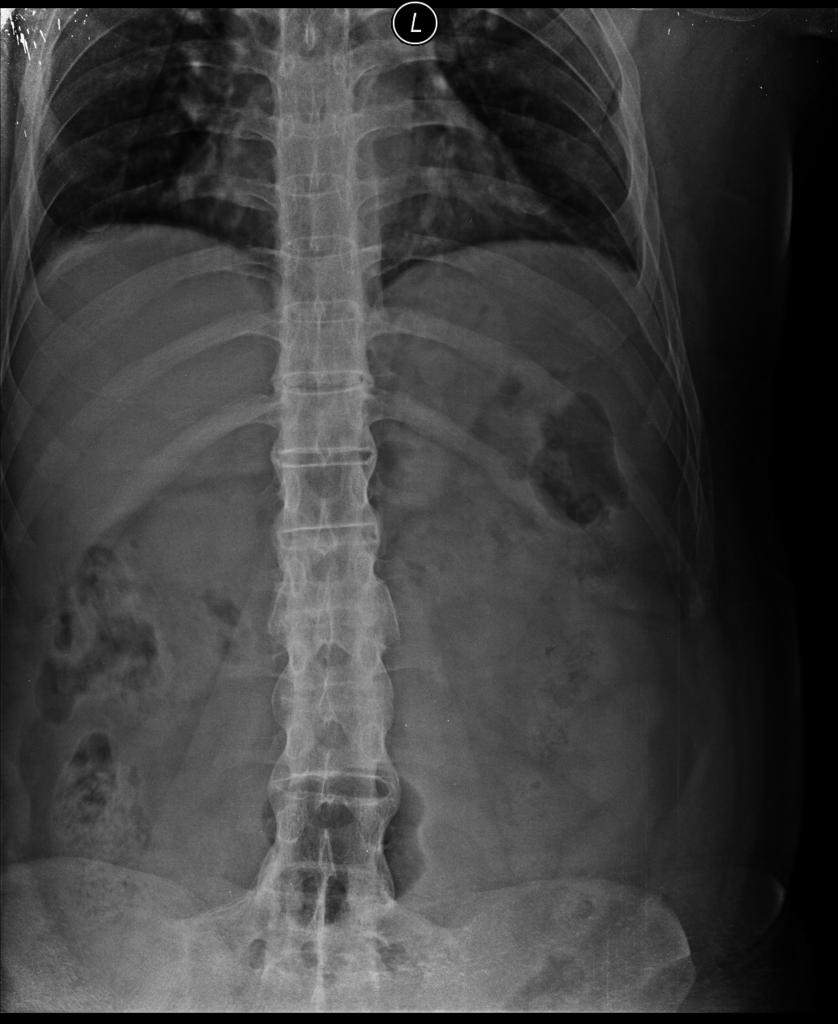
Ankylosing Spondylitis and How It Is Portrayed Radiographically
Clinical Presentation The patient is a 65-year-old female with a history of chronic low back and neck pain and markedly reduced mobility in the cervical and lumbar region. Her records have noted the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis for 20 years.

Ankylosing spondylitis "Romanus lesions" Image
Overview Ankylosing spondylitis, also known as axial spondyloarthritis, is an inflammatory disease that, over time, can cause some of the bones in the spine, called vertebrae, to fuse. This fusing makes the spine less flexible and can result in a hunched posture. If ribs are affected, it can be difficult to breathe deeply. Ankylosing spondylitis

Spinal injury in ankylosing spondylitis The BMJ
Patterns of radiographic involvement can be assessed using the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index (BASRI). Usually, symmetric sacroiliitis can be seen in 86% of patients, complete spinal fusion in 28% of patients for more than 30 years, and in 43% of patients with AS for more than 40 years. 13